Digestive discomfort or unexplained gastrointestinal symptoms often require specific diagnostic procedures to understand underlying causes. Two common methods used by gastroenterologists are esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) and colonoscopy. While both are invaluable diagnostic tools, they serve different purposes and focus on distinct regions of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Here is a breakdown of each procedure, outlining how they work, what to expect, and how they can benefit patients:
Contents
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
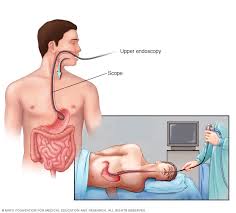
An EGD is a diagnostic procedure that examines the upper GI tract, which involves using a flexible tube called an endoscope equipped with a light and camera. This allows a gastroenterologist to inspect the esophagus, stomach visually, and the first part of the small intestine, called the duodenum, for abnormalities. EGDs are commonly recommended for individuals experiencing symptoms that may indicate upper GI issues. These symptoms often include persistent heartburn, difficulty swallowing, frequent nausea and vomiting, unexplained stomach pain or bloating, and symptoms of upper GI bleeding, like bloody stools.
How It Works
During an EGD, the patient typically lies on their side. The procedure begins with heavy sedation to minimize any discomfort, but you are awake. The gastroenterologist then guides the endoscope through the mouth and into the upper GI tract. Real-time imaging enables them to identify potential abnormalities such as inflammation, ulcers, or growths. The procedure can also include biopsies, allowing tissue samples to be collected for laboratory analysis. This can determine whether a patient has infections, celiac disease, or cancerous cells.
What To Expect
While still needing preparations, the EGD procedure is usually quick and performed as an outpatient service. Patients are asked to fast for several hours before the procedure to guarantee the upper GI tract is clear. Individuals are monitored briefly while the sedation wears off. Because of the sedative effects, a companion is required to provide transportation home. Some patients might experience a mild sore throat for a few hours after the procedure, but this typically resolves on its own.
Colonoscopy
A colonoscopy is a different diagnostic procedure that examines the lower GI tract, specifically the colon (large intestine) and rectum. It is used to detect issues such as inflammation, ulcers, abnormal growths (polyps), and signs of colorectal cancer. Colonoscopies are also employed for treatment purposes, such as the removal of polyps to prevent them from progressing into cancer. Gastroenterologists may recommend colonoscopies to monitor or diagnose a variety of conditions, including chronic diarrhea, unexplained changes in bowel habits, rectal bleeding, and abdominal pain.
What To Expect
Preparing for a colonoscopy generally involves a bowel-cleansing preparation to clear the colon, which the doctor will provide instructions for. The procedure is performed under sedation, similar to an EGD. During the process, the gastroenterologist inserts a flexible tube equipped with a camera, called a colonoscope, through the rectum to examine the colon.
The procedure allows the specialist to visually assess any abnormalities and remove polyps or collect biopsies if necessary. Like an EGD, the sedation means arranging transportation home is necessary. A colonoscopy generally takes 30 minutes, depending on the complexity of the case. Patients may experience mild bloating or cramping afterward, but this typically subsides quickly.
How an EGD and Colonoscopy Can Help You
EGD and colonoscopy provide valuable insights into gastrointestinal health, helping to diagnose and precisely monitor conditions. An EGD focuses on the upper GI tract, targeting symptoms such as persistent heartburn, difficulty swallowing, and stomach discomfort. A colonoscopy, on the other hand, is key for assessing the lower GI tract, addressing issues such as changes in bowel habits, rectal bleeding, and screening for colorectal cancer. Contact a specialist today to learn more about which procedure is right for you.

Sarah Wilson, an accomplished writer and seasoned blogger, weaves compelling narratives that transport readers to new and uncharted worlds. With a talent for vivid storytelling and thoughtful insight, her work leaves a lasting mark, enchanting both the imagination and intellect.