Skin cancer is among the most common cancers diagnosed in the United States. Spotting its symptoms early can make an impactful difference in treatment outcomes. Here is more information about skin cancer, what it may look like, and factors that contribute to its development.
Contents
What Is Skin Cancer?
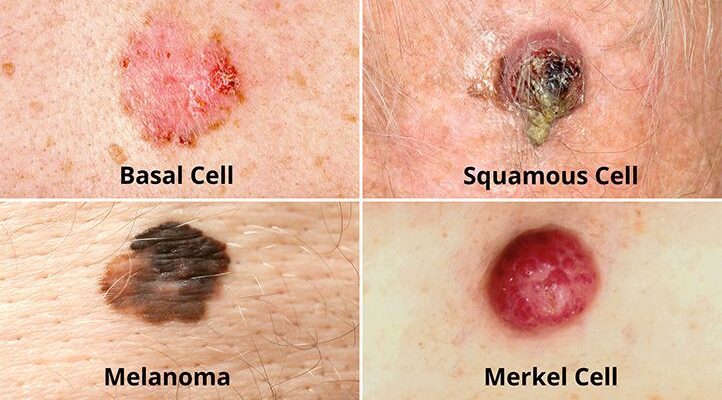
Skin cancer occurs when skin cells grow abnormally, often due to damage from ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds. There are three main types to know about. Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of cancer of the skin. It typically grows slowly and rarely spreads, but if left untreated, it can still damage surrounding tissue.
Squamous cell carcinoma, on the other hand, can grow deeper into the skin and has a higher risk of spreading if not addressed. The most aggressive form is melanoma, which can spread rapidly to other parts of the body and is responsible for the majority of skin cancer-related deaths. Routine self-checks and timely visits to a dermatologist can lead to early detection and successful treatment options.
What Does It Look Like?
Being aware of physical changes to the skin is key to identifying cancer in the skin. The symptoms may vary based on the type, but there are some common clues to watch out for. Basal cell carcinoma often presents as a pearly or waxy bump, but it can also appear as a flat lesion that is flesh-colored or brown. Squamous cell carcinoma, on the other hand, typically forms as a red, scaly patch or a firm, raised bump that may crust over or bleed. Melanoma is usually identified as a new mole or changes in an existing mole.
An effective way to monitor moles and other skin lesions is the ABCDE rule:
- Asymmetry: One half of the mole does not match the other.
- Border: Edges are irregular, jagged, or blurred.
- Color: There are multiple shades or an uneven distribution of color.
- Diameter: The mole is larger than 6 millimeters (about the size of a pencil eraser).
- Evolution: The mole changes in size, shape, or color over time.
Early detection saves lives. If you notice changes like these, seek medical advice for further evaluation.
What Causes It?
Certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing skin cancer. Spending a lot of time in the sun or using tanning beds exposes your skin to damaging UV rays. Those with fair skin, light-colored eyes, or blonde hair have less natural protection and may be at higher risk.
Having precancerous growths, such as actinic keratosis, or having several moles also raises the chances of skin cancer. Individuals taking immunosuppressant medications should be particularly cautious since their immune systems may have a reduced ability to fight abnormal cell growth.
Developing sun-safe habits, like wearing sunscreen and protective clothing, can help reduce risks. Regular skin examinations, either self-performed or by a professional, enable early detection of abnormal changes.
A Call to Action for Your Skin’s Health
Skin cancer is treatable when caught early. There are many treatment options that can effectively remove the cancerous tissue. Early intervention leads to better outcomes and lower recurrence rates. Take charge of your skin’s health by performing regular self-checks and scheduling routine dermatology appointments. Early detection and treatment can make a big difference. Stay proactive and protect your skin.